If you’ve been poking around your graphics card settings, you may have been wondering what GPU scaling is all about. What is AMD GPU scaling? What is Nvidia GPU scaling? The short answer to these questions is that GPU scaling is a graphics setting that lets you adjust the aspect ratio of your games to match your monitor’s resolution. It’s especially useful if you want to play a game that has a different native aspect ratio than your monitor.
In this guide, we will cover everything you need to know about GPU scaling, including whether you need it or not and how to enable and disable it.

What is GPU scaling?
GPU (graphics processing unit) scaling is a feature offered by both Nvidia and AMD cards. It mostly comes in handy in older games that may have been designed with 4:3 monitors in mind or without ultrawide support.
Most of the best gaming monitors operate on a 16:9 aspect ratio, but older games are not adapted to match that. When using emulators or simply just playing an old title, you’ll find that the majority of games have a different aspect ratio and were made for a different screen resolution.
Without GPU scaling, such older games often just look bad. Most commonly, the games are stretched to fit the native aspect ratio of the screen, and the end result is usually pitiful. When GPU scaling is enabled, the technology works to remedy that and make your games look their best once again.
What GPU scaling usually does is simply preserve the game’s original aspect ratio and create a border around it instead of forcing it to fit your monitor. However, there are two other modes that work around the problem in different ways — we explain them in more detail below.
In the case of Nvidia, GPU scaling is enabled through the Nvidia Control Panel, while AMD users can find the setting in either AMD Radeon Settings or the AMD Catalyst Control Center.
GPU scaling modes explained
Nvidia and AMD both offer different modes of GPU scaling, allowing you to adjust the experience to your needs. Let’s go over them quickly.
GPU scaling modes on AMD cards
AMD users can choose between the following GPU settings:
- Maintain Aspect Ratio: This setting lets you experience the game with the same aspect ratio as it was intended to be played, so a 5:4 game will remain 5:4. The excess parts of your monitor will be filled with a black background.
- Scale Image to Full Panel Size: This option will stretch the image to fit your screen, forcing it out of its intended aspect ratio. This setting will usually produce poor visuals.
- Use Centered Trimmings: This last AMD setting will center the game or the image in its original aspect ratio. The remaining parts of your screen will be filled with black bars or a background pattern.
GPU scaling modes on Nvidia cards
If you have an Nvidia card, you can choose between the following GPU scaling options:
- Aspect Ratio: Much like AMD, this will simply keep the game in its original aspect ratio. The excess space on your screen will be filled out with black bars.
- Full-screen: This setting will force the game to match your monitor’s aspect ratio. For example, a 5:4 game will turn to 16:9, if that’s what your display supports. Unfortunately, the end result is usually poor.
- No Scaling: As the name implies, this setting will turn off GPU scaling and will let the games render without interference.

GPU scaling — on or off?
If you’re a fan of indie games, retro games, or like to play on emulators, you may find some use for GPU scaling. Although many modern emulators simply run the games in their intended resolution, there are some that won’t. Older games, made long ago, don’t even have the perks of recently-released emulators and will simply look bad when played on 16:9 screens.
We recommend turning GPU scaling on and off on a case-by-case basis. If you’re about to launch a retro game, go ahead and turn it on — but remember to turn it back off when your gaming session comes to an end.
How to enable GPU scaling on Nvidia graphics cards
Turning on GPU scaling on Nvidia cards is easy and can be done in a few quick steps.
Step 1: Launch the Nvidia Control Panel
In order to change your GPU settings, you need to enter the Nvidia Control Panel.
You can do this by simply right-clicking on your desktop and then selecting Nvidia Control Panel from the drop-down menu.
Alternatively, enter the Windows Start Menu by clicking the Windows icon on the bottom-left side of the screen. You can also just press the matching Windows button on your keyboard. Once in the Start Menu, type in “Nvidia Control Panel” and then press Enter.
If you can’t find the Nvidia Control Panel, it may not be installed on your computer. Download it here, and then install the file to proceed.
Step 2: Find the GPU scaling settings
Once in the Nvidia Control Panel, navigate the menu on the left-hand side until you see the Display section.
Under there, search for the Adjust Desktop Size and Position. Click on it to find yourself in the appropriate part of the settings.
Step 3: Enable GPU scaling
There are a few settings that you can adjust here to tailor GPU scaling to your needs.
Start by finding the option titled Perform Scaling On. From the dropdown menu, select GPU.
Look back up toward Select a Scaling Mode and choose which option suits you best. If you’re not sure, we recommend picking the Aspect Ratio setting. For a refresher on what each setting does, click here.
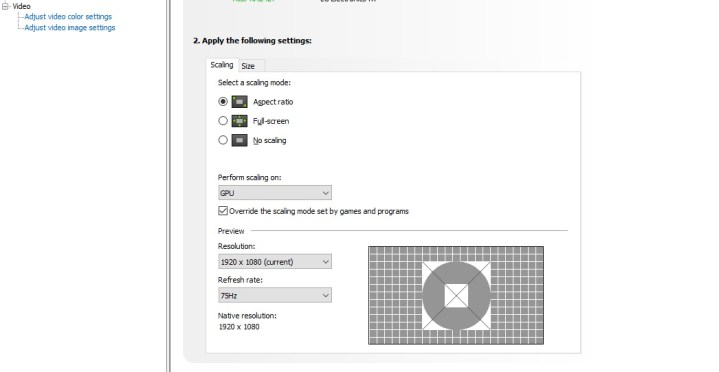
There is an interesting option here that you can consider if you run into problems with GPU scaling, called Override the Scaling Mode Set By Games and Programs. Leave this box unticked, but if you find that GPU scaling is not doing the trick, you can always try to enable this and see the results.
While you’re here, check the Resolution and Refresh Rate settings and set them both to the highest options available.
To save all the changes, press Apply.
Congratulations — GPU scaling is now enabled on your computer.
How to enable GPU scaling on AMD graphics cards: AMD Radeon Settings
You can use the AMD Radeon Settings to enable GPU scaling.
Step 1: Launch AMD Radeon Settings
Right-click anywhere on your desktop to produce a dropdown menu.
At the very top of it, you will find AMD Radeon Settings. Click it to launch the appropriate software.
Step 2: Navigate to AMD GPU scaling settings
Your AMD Radeon Settings window may look slightly different from our examples — it all depends on your graphics card and the drivers you have installed. However, the general placement of options should be the same.
If in doubt, make sure you update your drivers to the latest version.
At the top of the Radeon Settings, click the Gear icon, find an option called Display, and then enter that section to tweak your GPU scaling settings.
Step 3: Enable GPU scaling
Find the option titled GPU Scaling and switch that to On.
Right next to that setting, you can choose your preferred Scaling Mode. Click on it to produce a drop-down menu with three options to choose from. Here’s a refresher on what each of these does.
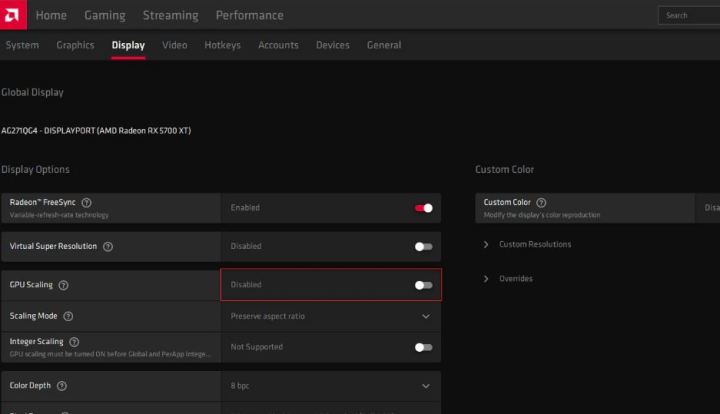
If you’re not sure what works best for you, the Maintain Aspect Ratio setting will generally be the best for most users.
Save the changes you just made to enable GPU scaling on your AMD graphics card.
GPU scaling FAQ
Does GPU scaling give more frames per second (fps)?
Unfortunately, while GPU scaling certainly makes retro gaming more enjoyable, it does introduce slight input lag.
What this means is that your fps will not be improved by using GPU scaling. In fact, it’s possible that your fps may be slightly lowered.
GPU scaling forces your graphics card to render each image and frame with additional effort, so this is bound to lower your fps a little bit.
Good news — if you’re playing old games, your fps should be high enough that you won’t even notice this. Alternatively, if you own one of the best graphics cards, your hardware is powerful enough to breeze through GPU scaling anyway.
Is GPU scaling good for new games?
There is no denying that GPU scaling is beneficial for retro games, or even newer games that for some reason were made with an unusual aspect ratio. However, when it comes to newer titles, you’ll find that GPU scaling can do more harm than good.
Compared to simply displaying the game as is, GPU scaling has to render the image from scratch and remake it to fit your monitor. This creates input lag, which can make for a less responsive gaming experience. It could even make you less competitive in multiplayer games.
Not only is GPU scaling harmful to newer games, but it’s also pretty much useless. When you’re gaming at the right resolution and aspect ratio, there’s no reason to use GPU scaling for anything at all.
As such, we recommend only enabling this setting for playing retro games and then turning it back off when you’re done.




