Speaking at the Chaos Communications Congress in Berlin, noted mobile security expert Karsten Nohl claims that all GSM mobile phones—that means about 80 percent of all mobile phones on the planet—are potentially vulnerable to attacks that can let others eavesdrop on conversations, as well as send texts and place calls from other people’s phones—potentially ringing up exorbitant changes to premium phone and text services. Although Nohl has not revealed the specific details of his method, he did note that hackers usually replicate the code needed for most mobile attacks within a few weeks.
“We can do it to hundreds of thousands of phones in a short timeframe,” Nohl told Reuters before his presentation. Nohl is the head of Germany’s Security Research Labs.
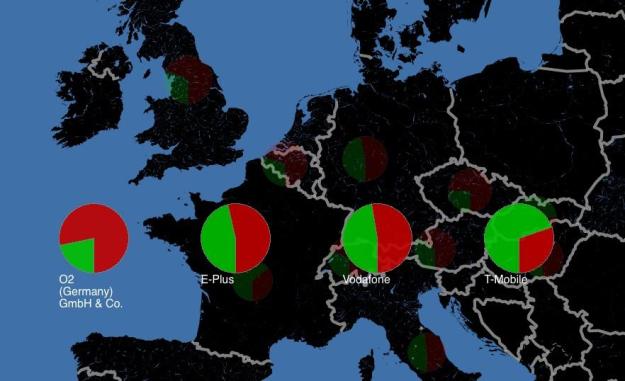
The exploit involves older 2G technology still widely deployed on many mobile operators’ networks. Nohl studied the operations of mobile carriers in 11 European countries using a seven-year-old Motorola phone, and was able to tap into both voice and text messaging from GSM users. Nohl also noted that, while it is possible for carriers to take steps from their GSM network’s command protocols from being misused, implementations vary widely between carriers, and even across regions. For instance, Nohl found that Vodafone’s British network was reasonably well locked down, its network in Germany was less secure. Germany’s T-Mobile and France’s SFR topped Nohl’s rankings.
A new Web site, gsmmap.org enables consumers to see how their carriers stacked up, and will soon enable interested users to participate in testing the security of their operators.
Mobile users in the United States may, ironically, be less vulnerable to these attacks than mobile users in many parts of the world since only two of the U.S.’s four major carriers—AT&T and T-Mobile—use GSM technology. Verizon Wireless and Sprint both use CDMA technology, which is not subject to this particular vulnerability.

